Small electric generators can be installed discreetly and go unnoticed by the Chinese government.
China: Hydro Generators Drop Price Due to Bitcoin Exodus. Reports indicate that, with China’s Bitcoin mining ban, prices for hydroelectric generators are plummeting on second-hand markets in that country.
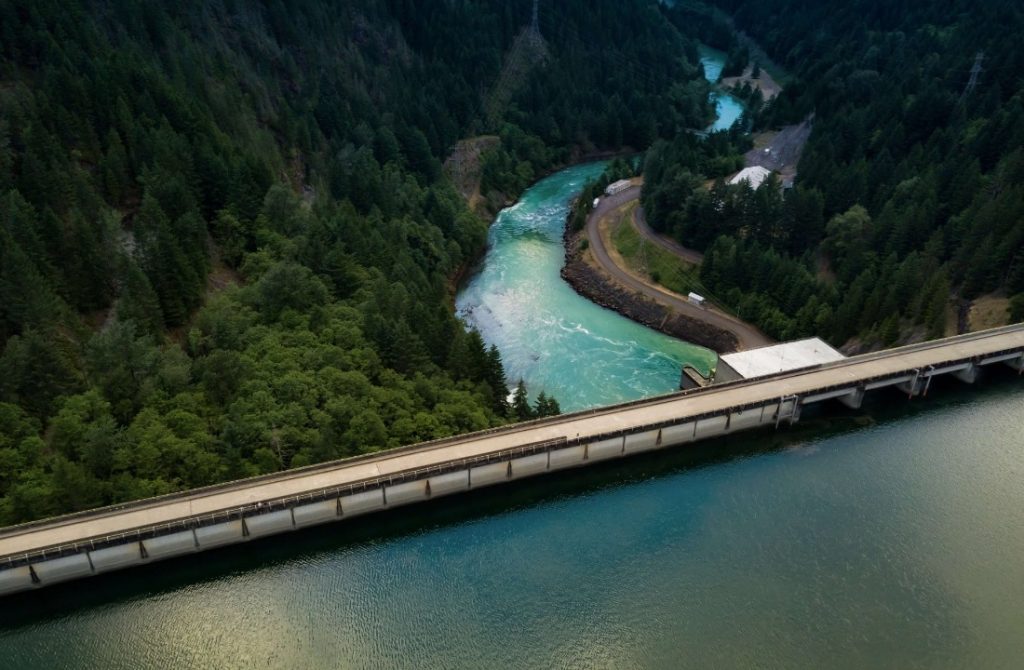
The South China Morning Post said that ads for small hydroelectric generators are rising on the popular e-commerce site Xianyu. The giant Alibaba owns it. People can install this kind of generator relatively easy to give Bitcoin miners power.
In China, authorities permit grants to the local private initiative to generate hydroelectric power. Hydroelectric generators can generate up to 50 megawatts (MW). They operate based on aquatic resources, abundant in some regions of China.
These generators are small in capacity compared to the more than 1,000 megawatts of power that at least some of the world’s large hydroelectric plants and power stations typically have. Even so, these small hydroelectric generators make it possible to supply energy to profitable activities such as Bitcoin mining.
According to the media outlet, public and private hydroelectric projects have also surged in the southwest region. However, some hydroelectric generator operators could have ventured into Bitcoin mining. They cannot supply the state electricity system due to a lack of permits.
According to the newspaper, the state argues that some hydroelectric generators have caused environmental problems, alteration of the course of rivers, and other ecological issues, so not all of them obtain permits or must repair the damage caused.
In addition, an SCMP source stated that, with these small hydroelectric generators, you could mine bitcoin anonmously, unnoticed by the authorities.
Bitcoin miners migrate from China.
The exodus of miners from China to other countries is developing in North America (the United States and Canada) and Central Asia (Kazakhstan and Iran, among other countries).
But just as with GPU graphics cards, which miners high demand of other cryptocurrencies, demand for hydroelectric generators may have dropped in China, causing prices to plummet as well. GPUs have also fallen in price because of China’s bans.
Also, not all miners will relocate in or out of China or resume operations to sell their ASIC equipment in international markets. This Bitcoin mining-only equipment could change ownership, further decentralizing this critical activity and industry for the protocol. Also, it could increase its availability in other parts of the world.
What is Bitcoin mining?
Mining cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin is similar (conceptually) to mining any mineral such as gold or coal. Instead of taking a pickaxe and wheelbarrow to extract value from the earth, you use computer programs and hardware to get value from the network.
When you mine cryptocurrencies, you put your hardware’s processing power at a network’s service, calling it Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Monero, etc. These cryptocurrency networks need the power of your hardware to confirm that their users’ transactions are valid. The network bundles all the valid transactions into a block and then adds them to the blockchain.
Adding new blocks to the chain earns you a reward of two parts: the commissions paid by the users who made the transactions included in the block plus the new coins generated. The system issued new cryptocurrencies with each new block, and you, who mined it, receive them. It’s as if your country’s central bank sent you freshly printed bills for lending to your computer, except that, when talking about Bitcoin, we are talking about really organic money.
In a nutshell, you can define the mining of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as a process in which a network’s transactions are validated, aggregated, and then added to its blockchain. This process provides security to the network while allowing the generation of new coins.
It is essential to mention that other networks validate their transactions with methods that do not require processing power. The distinction depends on the consensus algorithm used. Bitcoin uses a Proof of Work algorithm, while Cardano and others use a Proof of Stake approach.