Bitcoin is a money technology, the first drastic change since the creation of banking over 900 years ago. It has radical advances in money transfer, control, safekeeping, and supply and issuance.
Contents
What is the Bitcoin Cryptocurrency?
As described by its creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, in this technology’s defining document (read the Bitcoin White Paper [PDF]). Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer (p2p) electronic cash system. Every word of this definition is critical. First, it talks about a cash system and not only about cash, implying that Bitcoin is money (bills, coins, or any instrument to keep accounts between people.) It also explains the rules and mechanisms for creating and managing that cash. Using an analogy, Bitcoin is the dollar, the Federal Reserve, and the banking network, all at the same time.
Second, electronic cash points out that these “bills” or “coins” used money are not physical but digital. Computers create Bitcoin, transforming energy into money, meaning that while you can make a physical representation of that electronic cash, its original form is digital.
Finally, we speak of p2p or peer-to-peer to allude that Bitcoin has no central authority. No entity within this system is more powerful or has more privileges than another. In Bitcoin, anyone can participate in the system at any level. They can be a simple user of money through accounts (also known as crypto wallets). An auditor of the scenario through node software on their computer can also be an issuer of currency through mining equipment.
How does Bitcoin improve money?
There were only three ways to handle money: cash, bank accounts, and some PayPal-style companies. The first way, cash, is highly convenient for payments of small to medium amounts in person. For example, up to about a hundred dollar bills are instantaneous, private, and cost less. However, using cash becomes cumbersome for more significant amounts. Counting and verifying the bills and the space they take up, saving or storing cash, and the care taken to avoid damaging the bills. Finally, cash is seriously inconvenient to use for international transfers.
Ways two and three (banks and companies like PayPal) solve some of the drawbacks of cash but add other problems. A bank account helps dramatically save or move money. The user does not have to count or verify bills or find a place to store or carry them; these companies do that. This advantage allows easy remittances of large sums of money and international transfers. Although they are slow (they take days) and can be very expensive.
Apart from the problem of high costs, two other problems of profound importance are the lack of control of money and privacy in transactions. When using banks or companies such as PayPal, the money, in a certain way, ceases to be the owner’s property and becomes the property of these companies. How can this be verified? Easy. Try to move your money on a day that these companies do not work (such as weekends) or when you need it, and these companies say you can not use your money for any reason, such as lack of data or any policy they want to apply (See Canada blocking citizen accounts).
Financial User Privacy
Likewise, these companies register and scrutinize every movement the user makes with money. Depending on their policies, they decide what the user can or cannot do with “his money.” To top it off, the data they record of each transaction of their users is shared with third parties all the time (data companies to make money or government agencies are common examples).
Bitcoin, the fourth and best way to handle money today, changes everything. This technology blends the best of past worlds. It allows making transactions with the privacy and convenience of cash. Because it works digitally, it also allows you to save minor to large sums of money and move them to and from anywhere in the world. Best of all, at a low cost.
With Bitcoin, a person can open, at no cost, a digital account and store as much money as they want; if done correctly, their money will always be accessible to themselves and protected from access by others. Once you have your money in your Bitcoin account or wallet, you can move it 24/7/365 to other Bitcoin accounts worldwide in moments and with costs that approach zero, independent of where you send the transaction. These accounts include businesses where users purchase goods and services directly with BTC.
In short, Bitcoin makes money more accessible and cheaper to store and move, with greater security, control, and privacy for the owner and lower costs than any other system.
Who is behind Bitcoin?
Bitcoin defines how to manage money and money itself: electronic cash characteristics. So, just like a central bank, the Bitcoin system defines how many coins it issues and at what rate (supply control), with the difference of doing so regardless of demand. Whether many or few people want to use it, the Bitcoin system will keep issuing money at the rate agreed upon by the users without modifications to its programming.
In contrast, a central bank pretends to assess demand and modify the money supply accordingly, seeking to keep the value of its currencies “stable” (e.g., that a dollar is always worth a dollar in the market). Wrong money issuance is the leading cause of the world’s loss of purchasing power. The random and disproportionate increase in the money supply, by simple mathematics, only leads to the money as a whole being worthless. In other words, one peso buys a loaf of bread today and tomorrow. After printing, it is only enough for half a loaf.
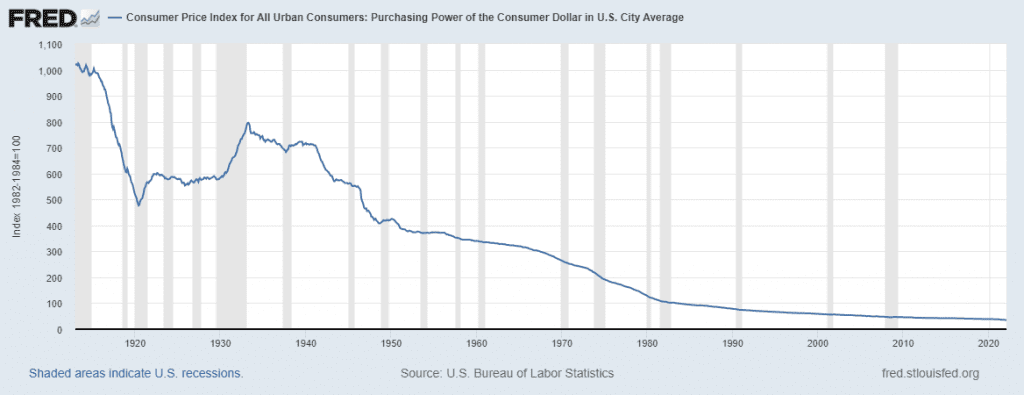

Money Supply
Bitcoin eliminates this problem by pre-scheduling the supply. Since it is defined from the beginning of the system how to issue new coins, the danger of losing purchasing power due to random and disproportionate printing disappears. Given this condition, the demand for bitcoins logically and predictably affects (at least in the long term) the price of money and, therefore, the purchasing power of those who have it: if more people use BTC than before, the price will rise; conversely, if fewer use it, its price will fall.
Moreover, unlike a central bank managed privately by a few people (even if it is an institution that affects the public), Bitcoin is managed by anyone. Anyone who wants to can “work” in this system, securing it, keeping the accounts, and issuing the coins.
Bitcoin Money Supply
The Bitcoin underlying algorithms fix the total supply of coins in the system. In 2140, Bitcoin it will reach its maximum 21 million bitcoins. Likewise, the issuance rate of these new coins (supply expansion) started at 50 bitcoins created approximately every ten minutes. The units issued halve every four years; for example, from 2020, 6.25 BTC are regularly issued, and by 2024, the reward will amount to 3.125 BTC.
How does Bitcoin work?
From a user’s point of view, Bitcoin works like a digital bank account. The user has an account or wallet to deposit money and withdraw it (send it) to another account. The user uses a “Bitcoin address,” similar to a bank account number, which is nothing more than a finite series of alphanumeric characters.
Types of Bitcoin addresses
Bitcoin addresses can come in different formats and, depending on this, allow the user to use more or less technological advances for managing their money. The difference is evident at the beginning of each address. Listed below are the most common formats, from the oldest to the most current:
Original format:
15e15hWo6CShMgbAfo8c2Ykj4C6BLq6Not
Format with simple expenditure conditions:
35PBEaofpUeH8VnnNSorM1QZsadrZoQp4N
Native Segwit format:
bc1q42lja79elem0anu8q8s3h2n687re9jax556pcc
Taproot format:
bc1pmzfrwwndsqmk5yh69yjr5lfgfg4ev8c0tsc06e
In the case of Bitcoin accounts or addresses, the money deposited is not just any currency but bitcoins (acronym BTC), the native currency of this system. BTC and any other currency take their value from other assets in the market. For example, a bitcoin worth 43,600 dollars (USD) on Friday, April 8, 2022, and 22.56 ounces of gold (XAU). Today it has another price.
Unlike the types of money we use in our day-to-day lives, such as the dollar or euro, whose values people believe to be stable, Bitcoin has sharp value changes over time. Volatility does not necessarily imply a problem. Since users are Internet-connected, buyers can know exactly how much bitcoin to receive or spend when paying for whatever.
Bitcoin is divisible
One BTC is the entire unit of one of the network’s “coins” or “bitcoins.” You can divide each bitcoin unit up to its hundred millionth part, i.e., up to 0.00000001 BTC, also known as one sat or satoshi.
From a system operator’s point of view, Bitcoin operates as a network of computers connected through the Internet. The blockchain is responsible for carrying out two main functions. One is to keep the system’s shared ledger up to date, synchronized, and in order. And two, to consolidate the transactions made by the system’s users and issue new coins.
The word “blockchain.”
It is essential to clarify a widely spread misconception before continuing. However, this only alludes to the ledger, an encrypted data file containing the history of transactions made on the network. In short, it is an essential part of the technology but does not replace it.
The “nodes” perform the first task. These ordinary computers run the Bitcoin software permanently to store the ledger. They also synchronize it with other nodes and keep it in order. Just as if you were to open WhatsApp and keep it on by synchronizing messages. Ensuring only to save those in a specific language.
Types of Bitcoin nodes
There are two types of nodes:– Full nodes, which run the Bitcoin software, store the ledger and keep it synchronized and in order. They also serve to send and receive bitcoin (BTC).
– Lightweight nodes, also known as Bitcoin wallets or accounts, serve to use bitcoin (BTC) without maintaining the network. They work by requesting the information they require for their transactions from full nodes.
The second task is performed by “miners.” These are also computers but specialized in carrying out a single task with very high performance. In this case, the task is to guess a number among infinite possibilities that allow it to compose a group or block of transactions sent by users under the rules established by the system and corroborated by the nodes.
Thousands of these computers worldwide compete to be the first to guess that number (technically called “nonce“). They try to win the reward for the correct block of transactions every 10 minutes as if it were a lottery. That reward comprises new coins issued by the system and fees paid by users for sending their payments.
Mining bitcoins at home
Although the Bitcoin mining industry is becoming more advanced, with more specialized equipment and larger farms, it is always possible to conduct the activity individually on a small scale in a profitable way, thanks to the nature of the Bitcoin system.
How to start using Bitcoin?
Getting started with Bitcoin is easy. You must create a digital account using some dedicated software, hardware, or website. Then, you must acquire bitcoins (BTC) using one of the many ways: through another person, at an exchange or bank, or an ATM. Each account and purchase option has advantages and disadvantages: cost, convenience, control, and security.
In the case of accounts or wallets, the easiest way to start is through a mobile application. The interested party should go to his phone’s app store (Google Play, AppStore, F-Droid, or other) and search for “Bitcoin.” You will find a sea of applications, and you can choose the one you like best.
Be careful when downloading Bitcoin wallets
When checking the phone’s store, it will show apps dedicated to private accounts, exchange or banking, and others that may be scams. When the user wants to have absolute control of his money, he should download a Bitcoin wallet or personal account app.
- If you need help choosing an application or system to manage your bitcoins, you can check the following link about the best bitcoin wallets.
- Check here for the best crypto exchanges to know where to buy bitcoins.
- Go to our crypto pricing page to see the bitcoin (BTC) price in your local currency.
- Finally, protect yourself from scams.
Once you have your account, please get familiar with it. See where the transactions are displayed, the balance, the receiving funds window, the sending window, and the settings section.
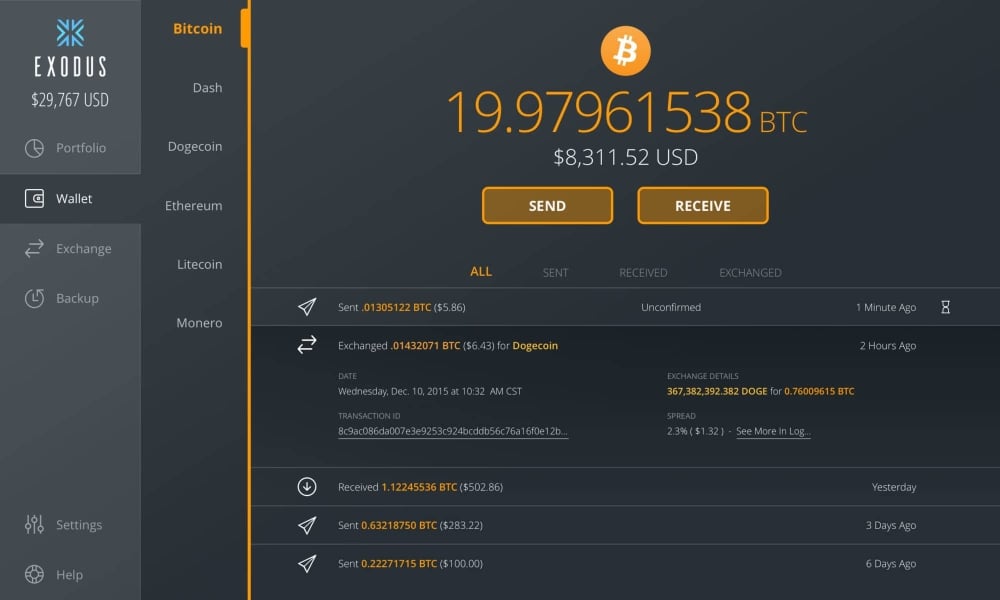

To acquire your first bitcoins and use this electronic cash system, you must give the person or institution with whom you are making the transaction the Bitcoin address of your account. Either copying and pasting it in text or showing it the QR code. Once your bitcoins are on your way, they will appear as an incoming transaction in your application. The transaction gets confirmed once the system has validated it.
All that remains with the bitcoins in your account is to say Congratulations! You can now use the most advanced money system in the world. Testing sending and receiving funds (preferably with little money) is advisable. It is better to become thoroughly familiar with and use the system correctly.
